A REVOLUTIONARY ADVANCEMENT IN ROCKET COMBUSTION
A NEW PARADIGM IN ROCKET COMBUSTION
AFRL’s Rotating Detonation Rocket Engine (RDRE) program is developing more efficient, compact and stable combustor designs for Liquid Rocket Engines (LREs).
The technology development approach integrates the state-of-the-art Modeling & Simulation (M&S) and experiments. A combination of DoD High Performance Computing Center clusters and cutting-edge diagnostics are employed to advance this revolutionary technology as quickly as possible for transition to the warfighter.
TECHNOLOGY TOOLKIT
- Laser combustion diagnostics: In-situ non-invasive ultra high-speed measurement of reaction zone and exhaust effluent composition to ascertain combustion efficiency in an unsteady flowfield.
- High-speed video diagnostics: Imaging of combustor wave dynamics coupled with robust post-processing extracts wave speed, number and operating mode.
- Additive manufacturing: Fabrication of regeneratively cooled hardware and novel injector configurations to promote steady and robust detonation wave propagation.
- Innovative chamber designs: Annular combustor geometry promotes seamless aerospike nozzle integration.
- High fidelity computations: 3D Large Eddy Simulations (LES) of RDRE experimental combustors provide insight into extreme detonation physics where conventional rocket sensors cannot survive.
- Digital engineering: Computational design of RDREs aids in prediction of as-built system and provides governance over automated fabrication.
KEY BENEFITS
- Detonation driven compression yields increased chamber pressures, producing greater propulsive thrust than conventional rocket engines
- Mitigation of combustion instability via detonative mode locking enables rapid design, development and transition to the warfighter
- Compact reaction zone reduces combustor length and weight, expanding rocket design space
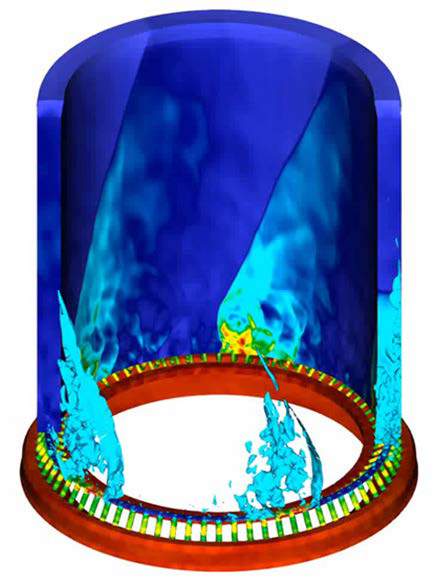

Cutaway image from a 5-million CPU-hour AFRL Large Eddy Simulation of the AFRL Gen-1 RDRE experiment. The propellant is injected at the bottom and exits the combustor at the top, with 5 co-rotating detonation waves (temperature color mapping shown) traveling from right-to-left along the back side of the annular combustor. The simulations accurately predict the performance and behavior of the physical experiments.
HARNESSING DETONATIONS FOR ROCKET PROPULSION
Rotating detonation is a more efficient type of combustion characterized by a closely coupled shock wave and reaction zone, where the fresh propellants are rapidly compressed, heated and burned. Nearly all chemical propulsion to date has used constant pressure combustion, or deflagration, to burn propellants in a subsonic flame. Rotating detonations in rocket propellants travel supersonically in excess of 2 km/sec (or 1 mile/sec), with part of the released energy feeding back into the shock wave to maintain continuous operation. RDREs can improve rocket performance for space launch vehicles, spacecraft and missile propulsion. This technology will support both USAF and USSF and will sustain and improve our nation’s leadership in space and missile propulsion.


AFRL Gen-1 RDRE testing at Edwards Air Force base in 2018 with gaseous
oxygen and methane propellants.

22,000 newton thrust (5000 lbf) RDRE testing with liquid oxygen and
gaseous methane testing by AFRL partner IN Space LLC at Purdue
University in 2021.
PARTNERSHIPS
AFRL’s in-house team and AFOSR partners laid the technological ground-work necessary to make RDRE’s a reality. In parallel, AFRL is collaborating with industry partners to accelerate development and transition the capability to National Security Space Launch for the warfighter. The team brings together established defense contractors with emerging aerospace companies.

GETTING INVOLVED
IPT membership is open to all stakeholders (or potential stakeholders) that are eligible to receive Distribution C information (U.S. Government agencies and their contractors).
Applicable white papers are considered through the AFRL Rocket Lab Hermes BAA (FA9300-20-S-0001), a two-step open BAA.